Orbitz360
With AR and VR in healthcare, You don't just get better—You get entertained!
Next stop, diagnosis land!
Overview
AR and VR are reshaping healthcare by providing immersive medical training environments for students and professionals, enabling precise surgical planning through 3D anatomical models, improving patient care with virtual therapies and pain management solutions, and enhancing rehabilitation programs with interactive exercises and progress monitoring. These technologies aim to optimize medical education, surgical outcomes, and patient recovery experiences through innovative virtual experiences.
Features
Immersive Medical Training
They provide realistic simulations where medical students and professionals can practice surgeries, medical procedures, and emergency scenarios in a controlled environment. Trainees can interact with virtual patients and medical equipment, gaining practical experience without the risks associated with real patients.
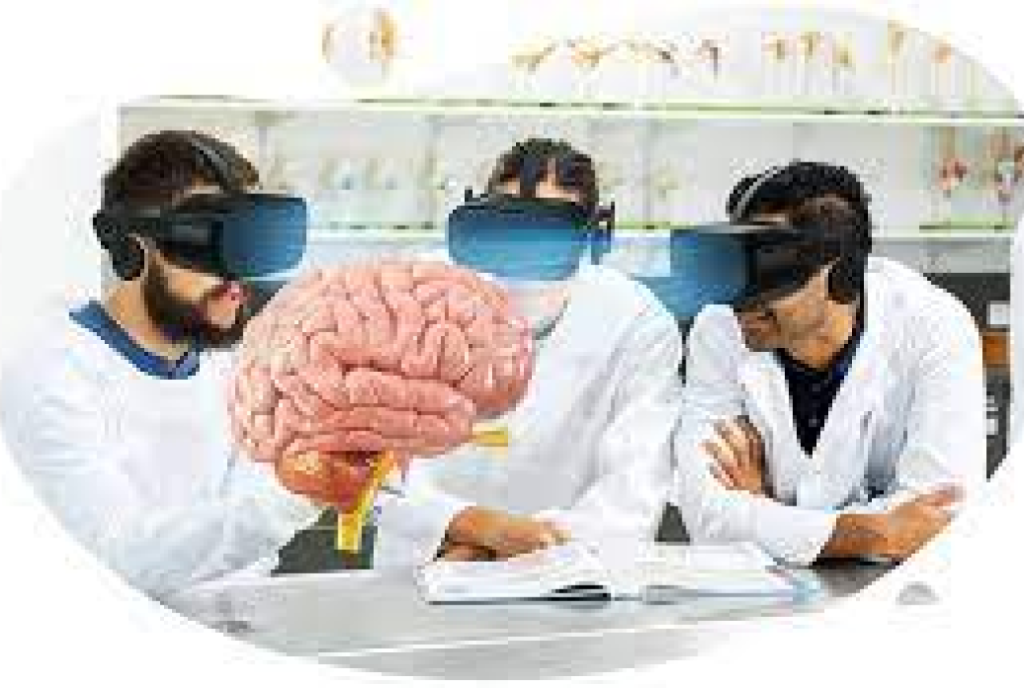

Precise Surgical Planning
Surgeons use AR and VR to create detailed 3D models of patient anatomy from medical imaging data. These models allow surgeons to visualize and plan complex surgeries, practice procedures, and anticipate potential challenges before operating on real patients.
Patient Care Enhancement
VR is utilized to distract patients from pain during procedures or treatments by immersing them in relaxing or engaging virtual environments. Virtual reality environments can help reduce anxiety in patients by providing calming experiences or distracting them during medical procedures.
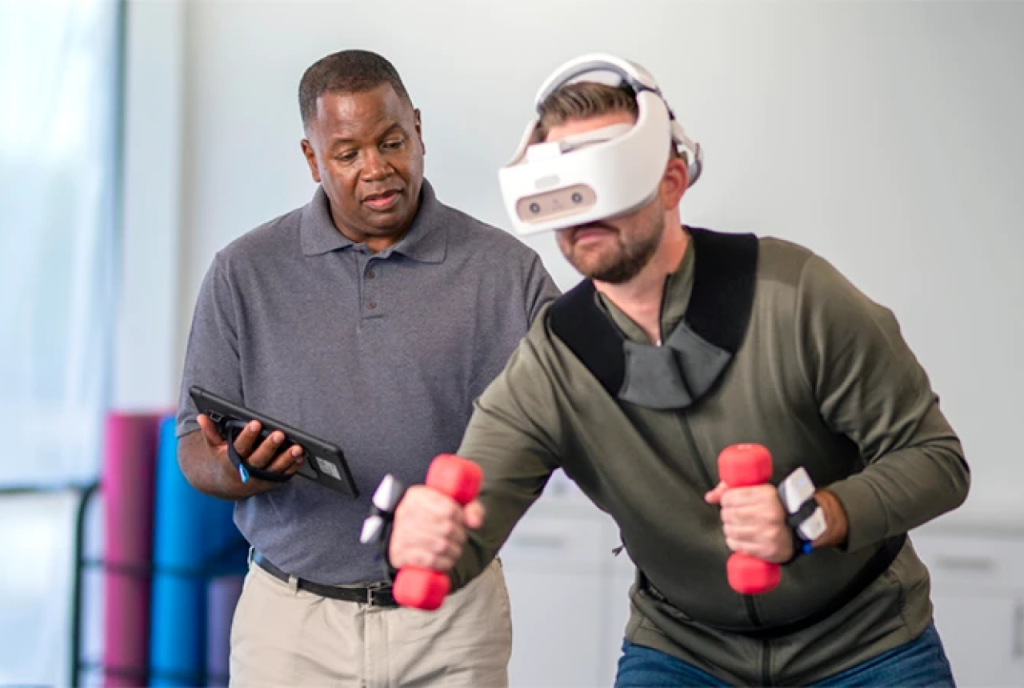


Rehabilitation Support
VR programs are used in physical and occupational therapy to engage patients in interactive exercises tailored to their rehabilitation needs. Therapists can track patients’ movements and progress over time, adjusting therapy programs accordingly to optimize recovery outcomes
Telemedicine Advancements
AR and VR enable remote consultations where specialists can virtually examine patients or collaborate with local healthcare providers, regardless of geographical distance.

Benefits
Research and Development
These technologies support advancements in medical research by providing new ways to study diseases, treatments, and patient responses in controlled virtual environments.
Cost Savings
By reducing the need for physical materials and facilities for training and therapy, AR and VR can potentially lower healthcare costs over time.
Remote Healthcare Access
AR and VR enable remote consultations and diagnoses, expanding access to specialized medical care regardless of geographical location.
Patient Engagement and Empowerment
They empower patients by involving them more actively in their own healthcare journeys. They can better understand their conditions through immersive visualizations, participate in their treatment plans, and feel more confident in their recovery processes.
Orbitz360 is proudly powered by WordPress
